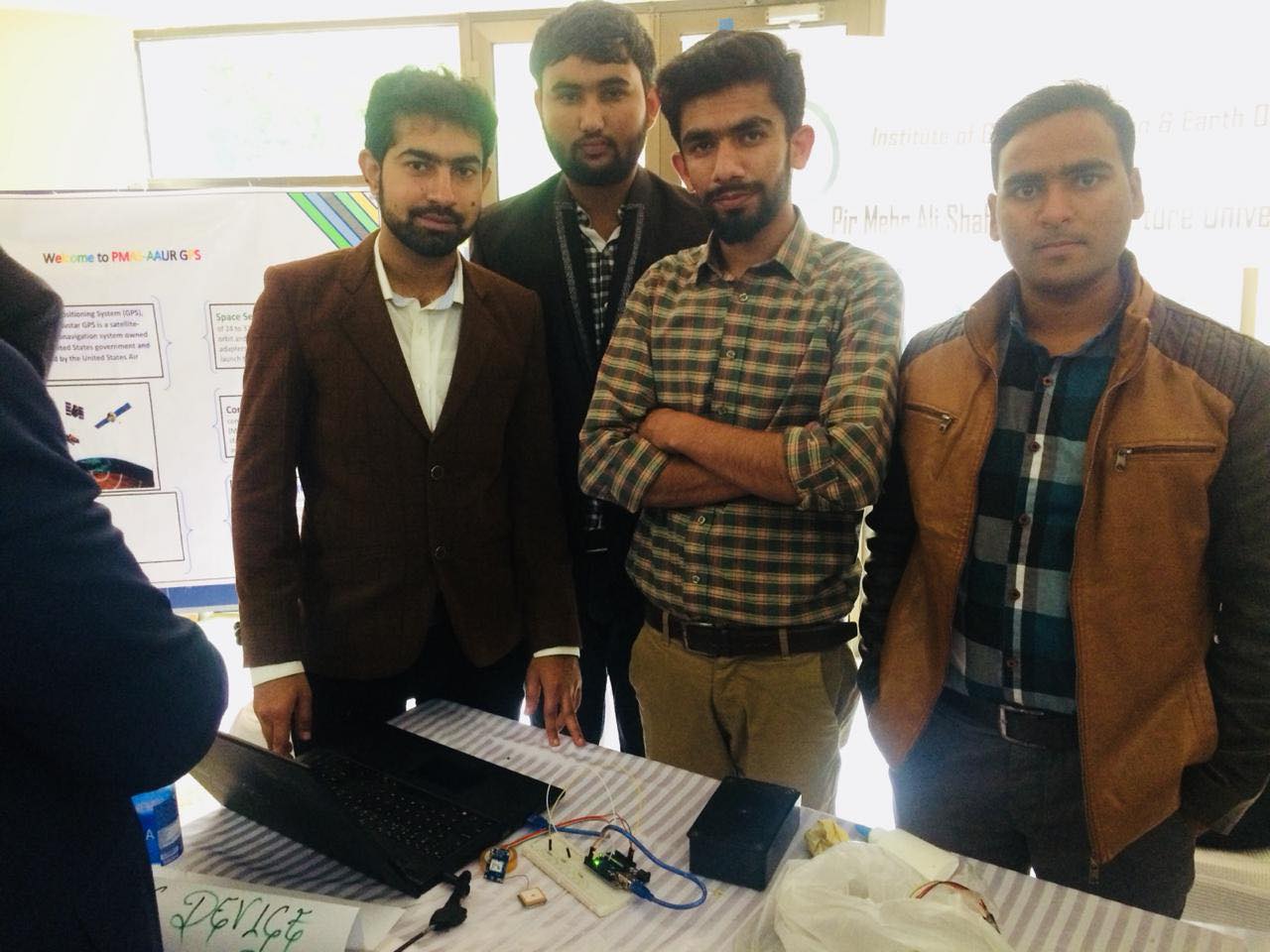

GPS NEO 6M Making using Arduino
DECODING GNSS SIGNALS (NMEA) TO READ LAT LONG USING NEO-6M



Team Members:
Muhammad Hamza
Khurram Khan
Waqas Jutt
Afsheen Sheikh
Advisors:
Naeem Malik (Lecturer)
Affiliation:
Arid University
Course:
GEODATABASE
Team Members:
Muhammad Hamza
Khurram Khan
Waqas Jutt
Afsheen Sheikh
Advisors:
Naeem Malik (Lecturer)
Affiliation:
Arid University
Course:
GEODATABASE
Introduction:
The Arduino GPS project aimed to develop a GPS tracking system using the NEO-6M GPS module and Arduino Uno. This report details the process of connecting the GPS module, obtaining raw GPS data, parsing the data to extract relevant location information, and the historical background of the project. The Arduino GPS project was undertaken during the 4th semester at BS GIS ARID University Rawalpindi, Pakistan, in November 2018. The project team consisted of Muhammad Hamza, Waqas Iftikhar, Khurram Khan, and Afsheen Sheikh. The project was presented at NUST GIS Day 2018, held at NUST Main Campus Islamabad. The inspiration for this project came from a desire apart from just doing a semester project, we should contribute to the field of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and make a positive impact on the world. The project was initiated by a discussion with a faculty member, Dr. NAEEM MALIK who encouraged students to explore innovative GIS-related projects. This led to the formation of project groups, and our team began brainstorming ideas for a unique and creative project that would also encompass GIS concepts.
How GPS Works
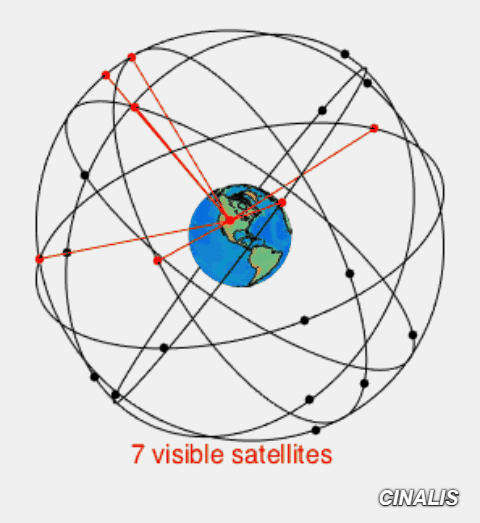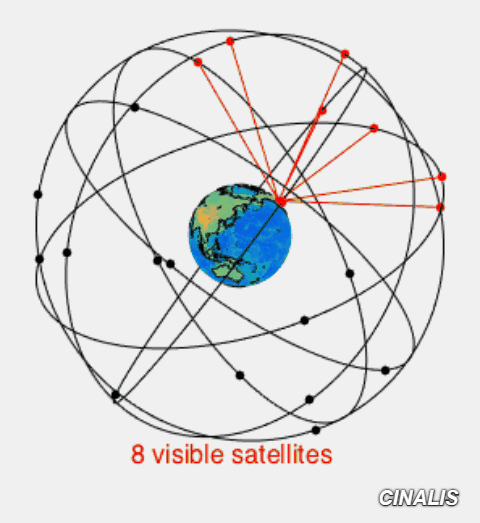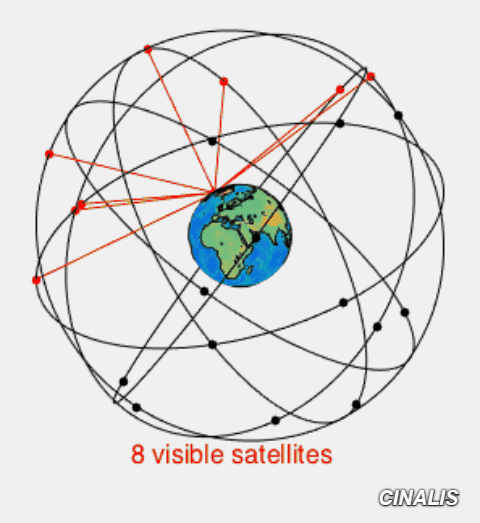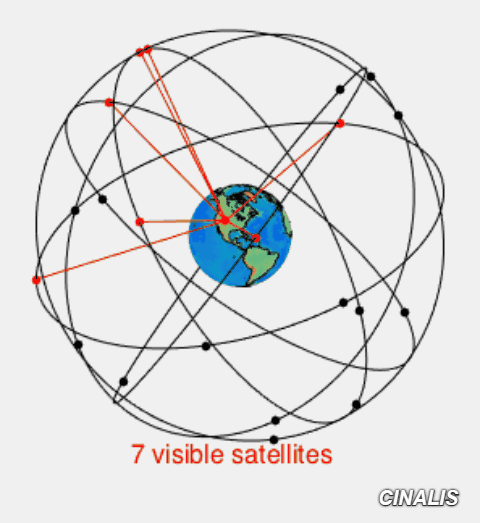
Signal path of GNSS from and to Ground Station
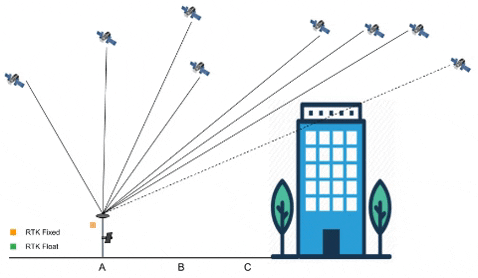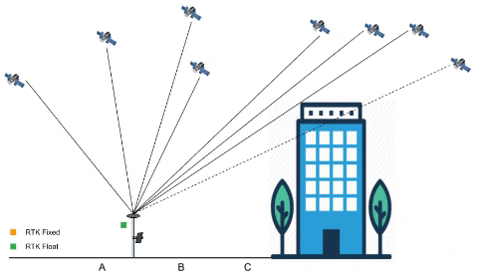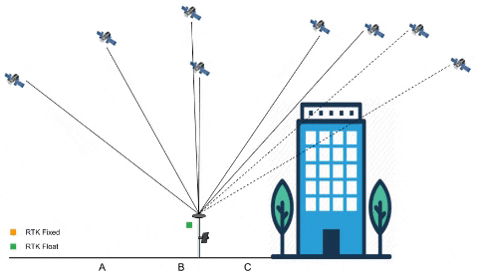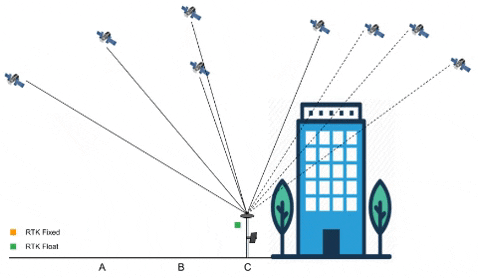
Project Development:
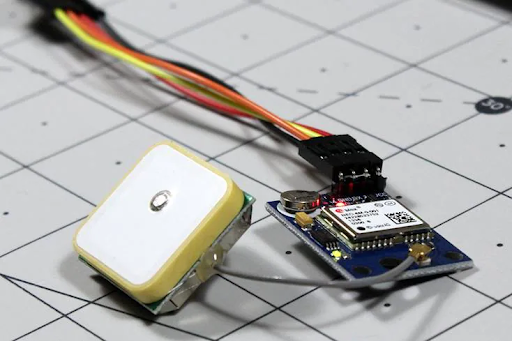
Procurement of Components To kickstart the project, essential components were procured. These components included an Arduino Uno, NEO-6M GPS module, various cables, boards, and electronic components. The team also acquired an external antenna to enhance GPS signal reception. Familiarization with Arduino As students with limited hardware experience, the initial phase of the project involved getting acquainted with Arduino. Tutorials, resources from YouTube, Google, and the official Arduino website were extensively utilized. The team conducted experiments with LEDs, bulbs, and motors to build foundational knowledge in hardware programming.
Methods:
Circuit diagram of GPS
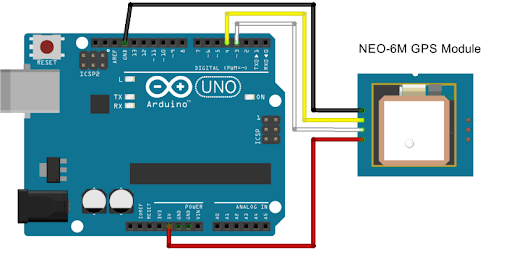
1. Assemble Components: Gather an Arduino Uno, Neo 6M GPS module, cables, breadboard (if needed), and an external antenna.
Maps:
Understanding NMEA Sentences
NMEA sentences, the standard data format used by GPS modules, were introduced. Each NMEA sentence was explained, with examples provided. The report clarified the structure of NMEA sentences, including their starting character ($) and comma-separated data fields.
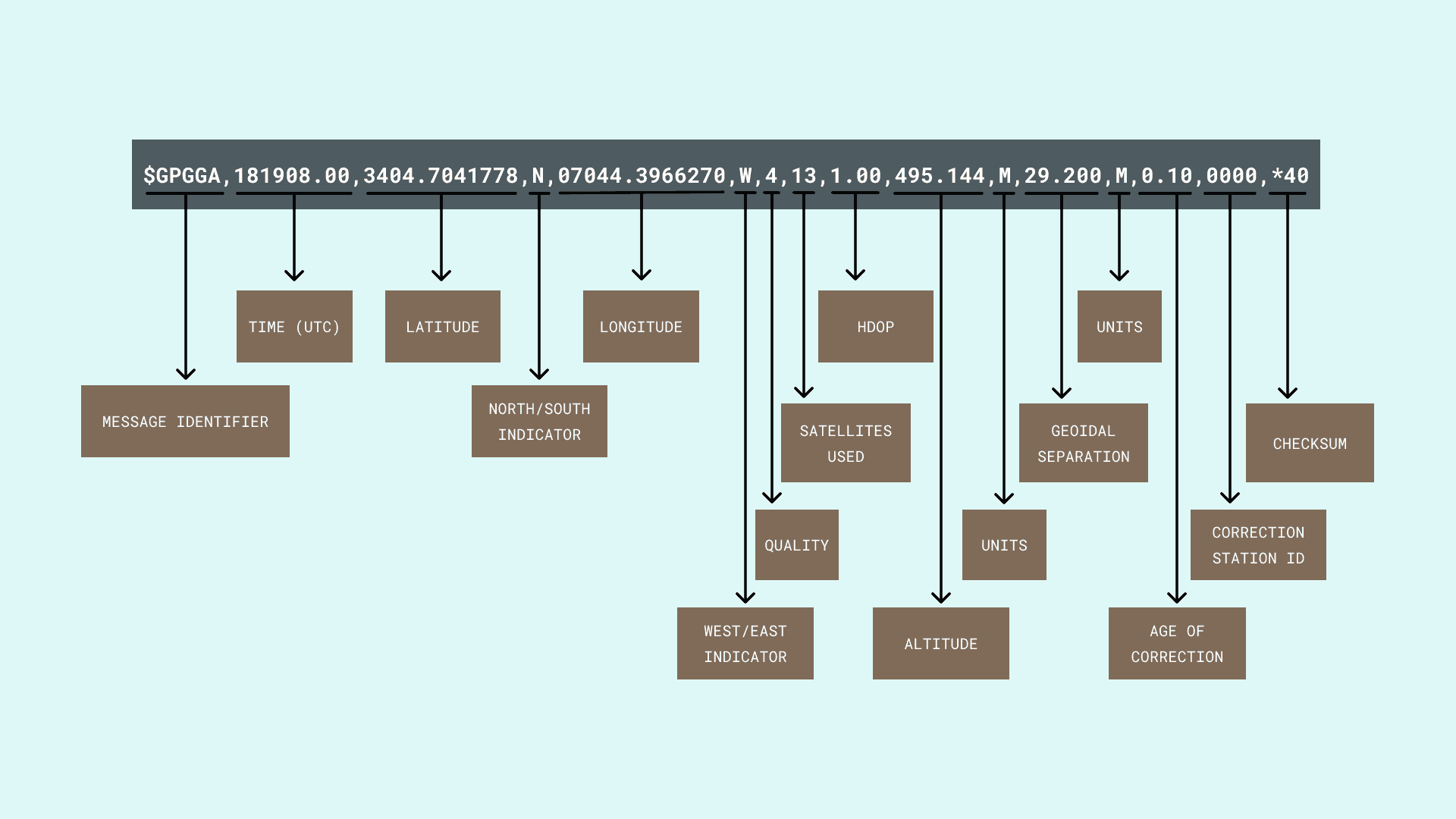
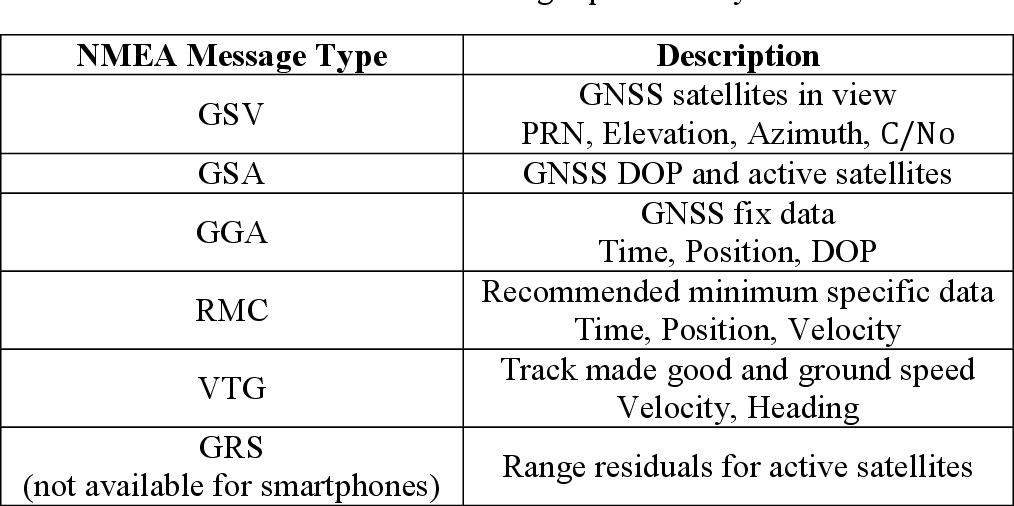
Discussion:
The Arduino GPS project successfully demonstrated the integration of the NEO-6M GPS module with an Arduino Uno and the use of the TinyGPS++ library to extract meaningful GPS information. The knowledge gained from this project laid the foundation for future.
Project Deliverables:
Code:
Please feel free to contact me at my email address or through my LinkedIn Account below.
mhwahla360@gmail.com